What is Weaving?
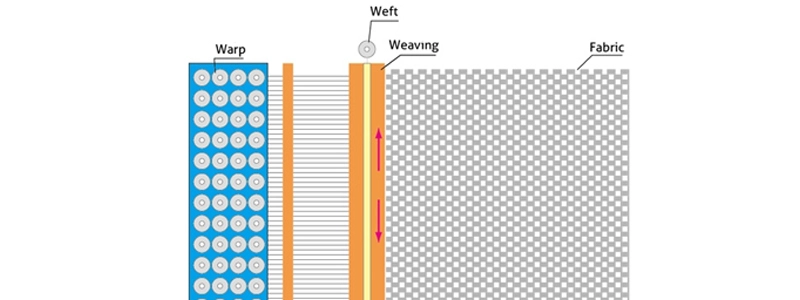
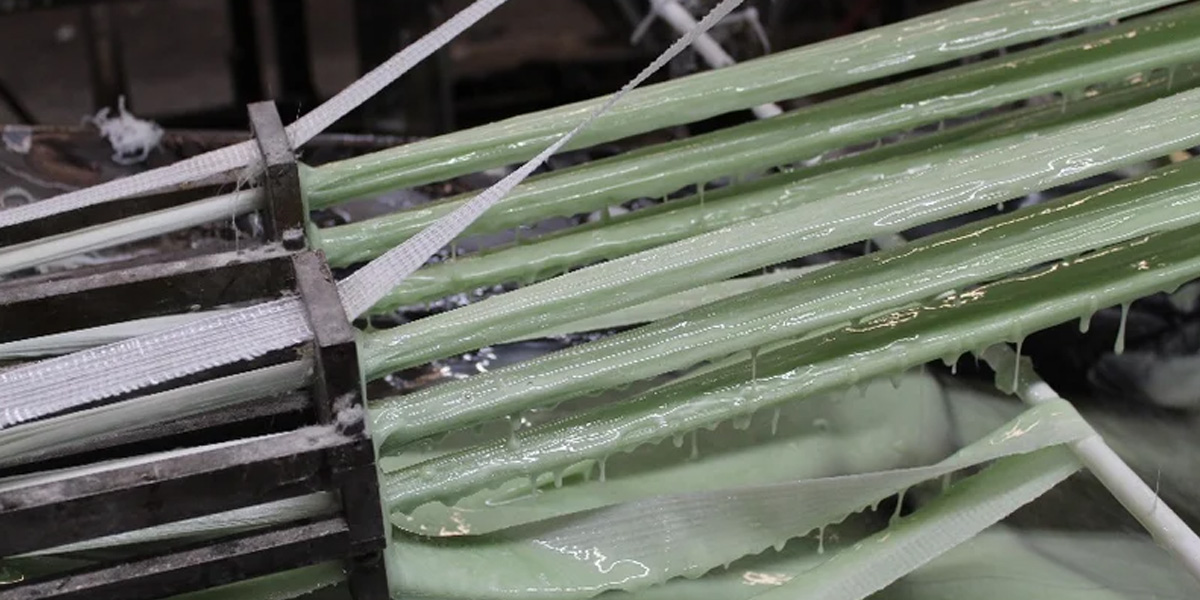
Weaving is a manufacturing process that involves interlacing two or more sets of yarns or fibers to create a fabric or textile. The process is often used to create composite materials with specific properties, such as strength, stiffness, and durability.
How does Weaving work?
The Weaving process involves the following steps:
- Yarn preparation: The yarns or fibers are prepared and wound onto spools or cones.
- Warping: The yarns are warped, or stretched, onto a loom or weaving machine.
- Wefting: The yarns are woven, or interlaced, with the warp yarns to create a fabric or textile.
- Finishing: The fabric or textile is finished, or treated, to enhance its properties and performance.
Advantages of Weaving
- High strength-to-weight ratio: Woven composite materials exhibit a high strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical.
- Improved impact resistance: Woven composite materials have improved impact resistance compared to traditional materials.
- Corrosion resistance: Woven composite materials are resistant to corrosion and can withstand harsh environments.
- Increased design flexibility: Weaving allows for complex geometries and designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing processes.
Applications of Weaving
- Aerospace industry: Woven composite materials are used in the aerospace industry for lightweight components, such as aircraft structures and interior panels.
- Automotive industry: Woven composite materials are used in the automotive industry for applications such as body panels, chassis components, and interior trim.
- Industrial equipment: Woven composite materials are used in industrial equipment, such as machinery components and structural frames.


